
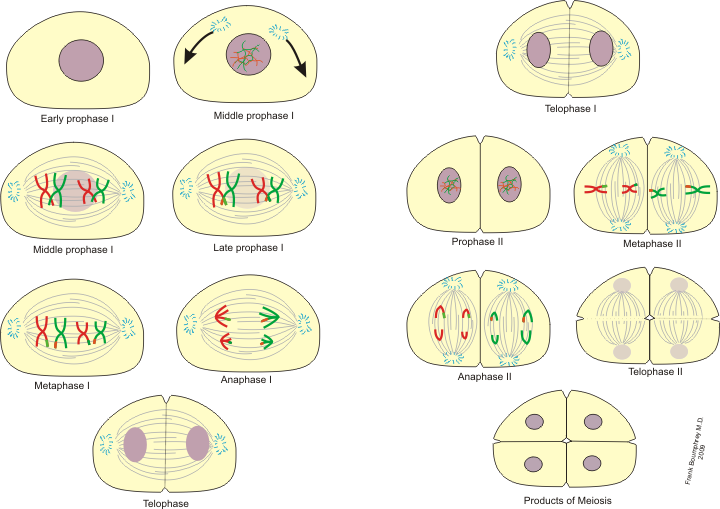
In animal cells, the appearance of furrows in the plasma membrane deepens gradually and joins to divide cytoplasm into two parts.Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm of a cell after karyokinesis i.e, division of chromosomes into two daughter cells.Nucleolus, Golgi complex and ER reappear.The nuclear membrane reassembles around the chromosome clusters.Chromosomes cluster at opposite spindle poles and their identity is lost as discrete elements.Telophase is the last stage of mitosis which involves.Two chromatids start moving towards opposite poles.Splitting of each chromosome at centromere into two sister chromatids.Chromosomes arrange at the centre of the cell called the metaphase plate.Condensation of chromosomal materials into compact and distinct chromosomes made up of two sister chromatids attached with spindle fibres with kinetochores.It starts the complete disintegration of the nuclear envelope hence the chromosomes are spread through the cytoplasm of the cell.Cells at the end of prophase, do not show Golgi complexes, endoplasmic reticulum, nucleolus and the nuclear envelope.Initiation of the assembly of the mitotic spindle, the microtubules, the proteinaceous components of the cell cytoplasm help in the process.Chromosomes composed of two chromatids attached together at the centromere.Chromosomal material condenses to form compact mitotic chromosomes.The following characteristic events take place in prophase: Prophase which is the first stage of mitosis follows the S and G2 phases of interphase. Mitosis has been divided into four stages of nuclear division: PROPHASE The number of chromosomes in the parent and progeny cells is the same, it is also known as equational division. During the S phase, the amount of DNA per cell doubles but the chromosome remains the same.
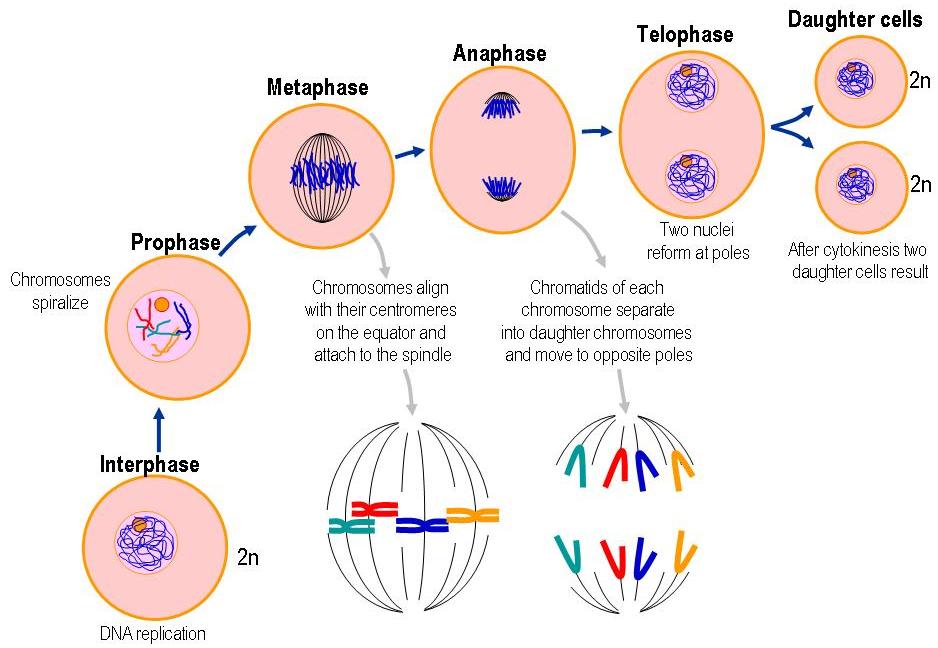
The cells that do not divide later exit the G1 phase to enter an inactive stage termed as quiescent stage (G0) of the cell cycle.Cells present at the G0 phase to enter in the G1 phase need to enter in a specialized gate present in the g1 phase to act as restriction entry.The cell cycle is divided into two basic phases: The sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its genome synthesises the other constituents of the cell and eventually divides into two daughter cells is known as the cell cycle.All these processes, i.e., cell division, cell growth and DNA replication, hence, have to take place in a coordinated way.It is a very important process in all living organisms.It is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells.Cell Division: Meiosis and Mitosis FAQs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
